Introduction
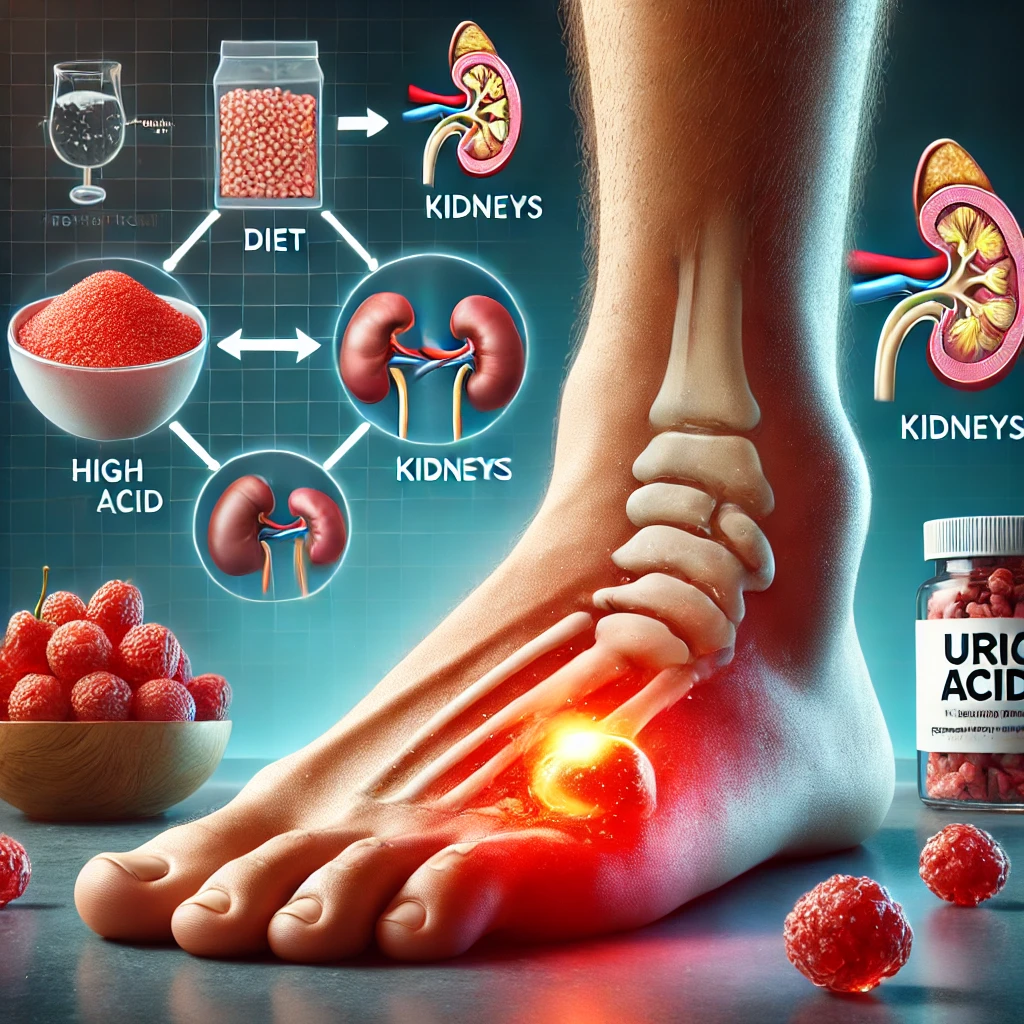
Gout is a common form of arthritis caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood, leading to painful joint inflammation. In Nepal, gout is becoming increasingly prevalent due to dietary habits, genetic factors, and lifestyle changes. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management of gout can help prevent complications and improve quality of life.
What is Uric Acid?
Uric acid is a waste product formed when the body breaks down purines, which are found in certain foods and also produced naturally in the body. Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood and is excreted through urine. However, when the body produces too much uric acid or fails to eliminate enough of it, uric acid crystals can accumulate in the joints, leading to gout.
Causes of High Uric Acid Levels
- Dietary Factors: High consumption of purine-rich foods such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and alcohol (especially beer and hard liquors) increases uric acid levels.
- Dehydration: Insufficient water intake can reduce the kidneys’ ability to flush out uric acid.
- Genetics: Some people inherit a tendency to have high uric acid levels.
- Obesity: Excess body weight is associated with increased uric acid production.
- Medical Conditions: Kidney disease, diabetes, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome can contribute to higher uric acid levels.
- Certain Medications: Diuretics and some other medications can interfere with uric acid elimination.
Symptoms of Gout
- Sudden, severe pain in a joint, most commonly in the big toe, ankles, knees, elbows, or fingers.
- Redness, swelling, and warmth in the affected joint.
- Pain that worsens at night or after consuming certain foods.
- Recurring gout attacks if not managed properly.
Diagnosis
Doctors diagnose gout through:
- Blood Tests: Measuring uric acid levels in the blood.
- Joint Fluid Analysis: Checking for uric acid crystals in joint fluid.
- X-rays or Ultrasound: Identifying joint damage or crystal deposits.
Managing and Preventing Gout
Lifestyle Changes
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help flush out excess uric acid.
- Balanced Diet: Reduce intake of high-purine foods and consume more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products.
- Limit Alcohol and Sugary Drinks: Alcohol and fructose-containing beverages can raise uric acid levels.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing weight can lower uric acid levels and reduce gout attacks.
- Exercise Regularly: Staying active helps with weight management and overall health.
Medical Treatment
- Pain Relief: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, or corticosteroids can help manage pain during attacks.
- Uric Acid-Lowering Medications: Drugs like allopurinol and febuxostat can reduce uric acid levels and prevent gout attacks.
- Proper Kidney Care: Since the kidneys help eliminate uric acid, maintaining good kidney health is crucial.
Conclusion
Gout is a painful but manageable condition. With proper dietary choices, lifestyle changes, and medical guidance, individuals can control uric acid levels and prevent gout attacks. If you experience frequent joint pain, swelling, or other symptoms of gout, consult a doctor for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Stay informed, stay healthy!
📞 01-4531078 or 01-4543386