Understanding Tonsils: Common Misconceptions and When to Seek Help
In Nepal, there is a common misconception regarding tonsils. The term “tonsil” is often used to refer to throat pain, leading to confusion. Many people avoid visiting a doctor for minor symptoms like sore throat or fever, and self-medication—especially the misuse of antibiotics from local pharmacies—is widespread. This has contributed to antibiotic resistance and a misunderstanding of tonsil-related conditions.
What Are Tonsils?
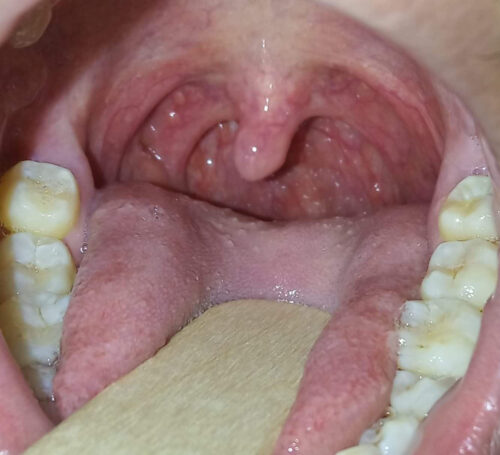
Tonsils are two oval-shaped masses of lymphoid tissue located at the back of the throat. They are part of the immune system and help detect and fight infections. Having tonsils is normal and does not mean you have an infection.
What Do Healthy Tonsils Look Like?
Normal tonsils are pink, symmetrical, and may vary in size. Some individuals naturally have larger tonsils, which is not necessarily a problem. However, if one tonsil is significantly larger than the other (asymmetry), it is advisable to consult an ENT specialist.
Common Tonsil Conditions
- Tonsillitis: Inflammation of the tonsils, usually caused by an infection.
- Tonsillar Hypertrophy: Enlargement of the tonsils, which may cause breathing or swallowing difficulties.
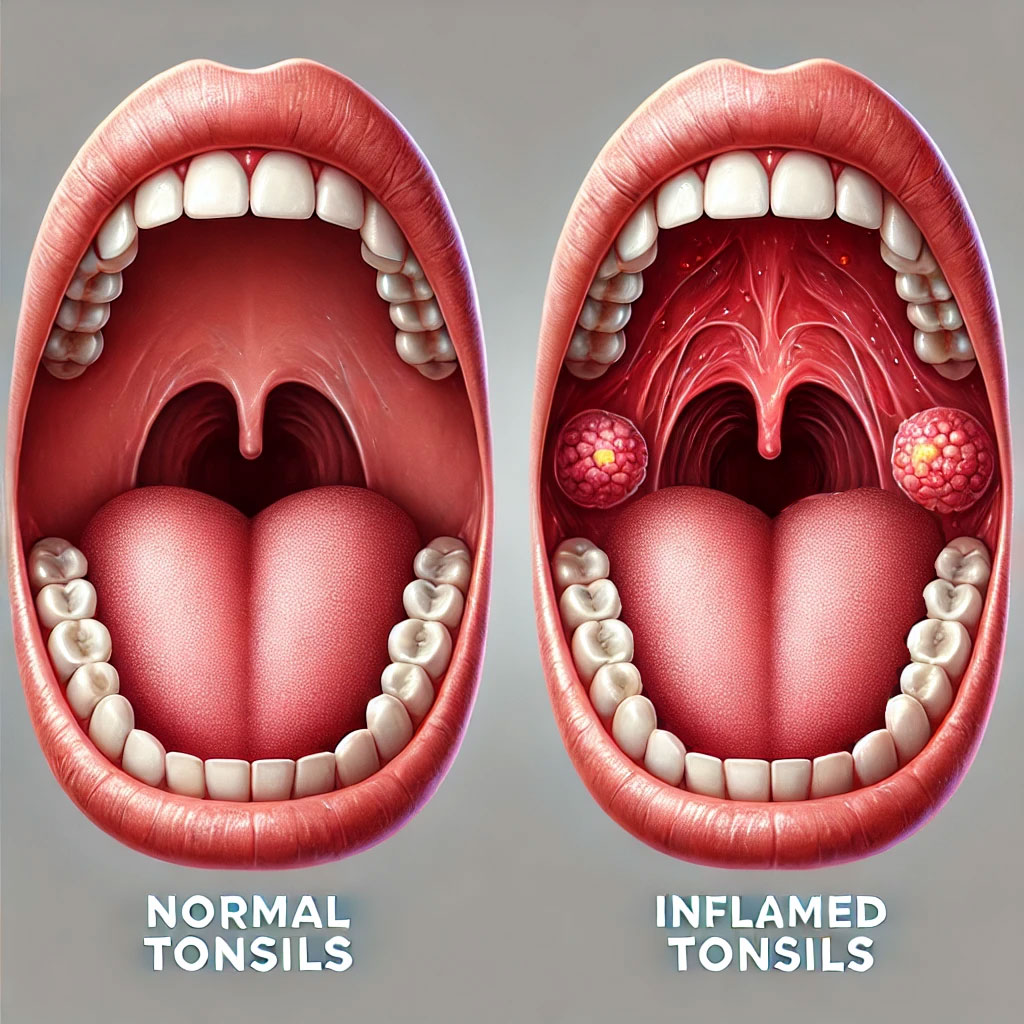
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
- Severe throat pain
- Fever
- Painful swallowing
- Enlarged, tender lymph nodes in the neck
- Red, swollen tonsils with white or yellow spots
- In young children: fever, excessive crying, refusal to eat
Symptoms of Enlarged Tonsils (Common in Children)
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Snoring and choking during sleep (sleep apnea)
- Excessive drooling
- Daytime sleepiness and poor school performance
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the above symptoms, seek medical advice. Not all sore throats are caused by tonsillitis; other conditions like viral pharyngitis, acid reflux, or throat ulcers can also cause throat pain and may not require antibiotics.
Causes of Tonsillitis
Tonsils help fight infections by trapping bacteria and viruses. However, when too many infectious agents accumulate, it can lead to tonsillitis. The most common causes are:
- Viruses
- Bacteria, particularly Group A Beta-Hemolytic Streptococcus (which can cause strep throat)
Can Tonsillitis Affect the Heart?
In most cases, tonsillitis does not affect the heart. However, untreated bacterial tonsillitis, particularly strep throat, can lead to rheumatic fever, an immune reaction that may damage the heart valves. Symptoms of rheumatic fever include joint pain, skin rashes, abnormal movements, palpitations, and shortness of breath. In Nepal, undiagnosed streptococcal infections contribute to rheumatic heart disease, especially among children and teenagers, with a higher prevalence in females.
When Should Tonsils Be Removed?
Tonsillectomy (surgical removal of the tonsils) is only recommended in specific cases, such as:
- Recurrent tonsillitis
- In children: 7 or more episodes per year, 5 or more episodes per year for 2 consecutive years, or 3 or more episodes per year for 3 consecutive years
- In adults: 3-5 severe episodes per year that interfere with daily activities
- Tonsillar enlargement causing breathing difficulties, snoring, or sleep apnea
- Recurrent peritonsillar abscess (two or more episodes)
- Asymmetrical tonsils, which may indicate malignancy (cancer)
Does Tonsil Removal Weaken Immunity?
There is no conclusive scientific evidence that removing tonsils significantly weakens the immune system. However, tonsillectomy should only be performed when medically necessary.
Author

Dr. Bigyan Raj Gyawali, M.B.B.S, M.S, MRCS-ENT (U.K.), FICS
Consultant ENT, Head & Neck Surgeon
Advanced Polyclinic, Kathmandu, Nepal