Introduction
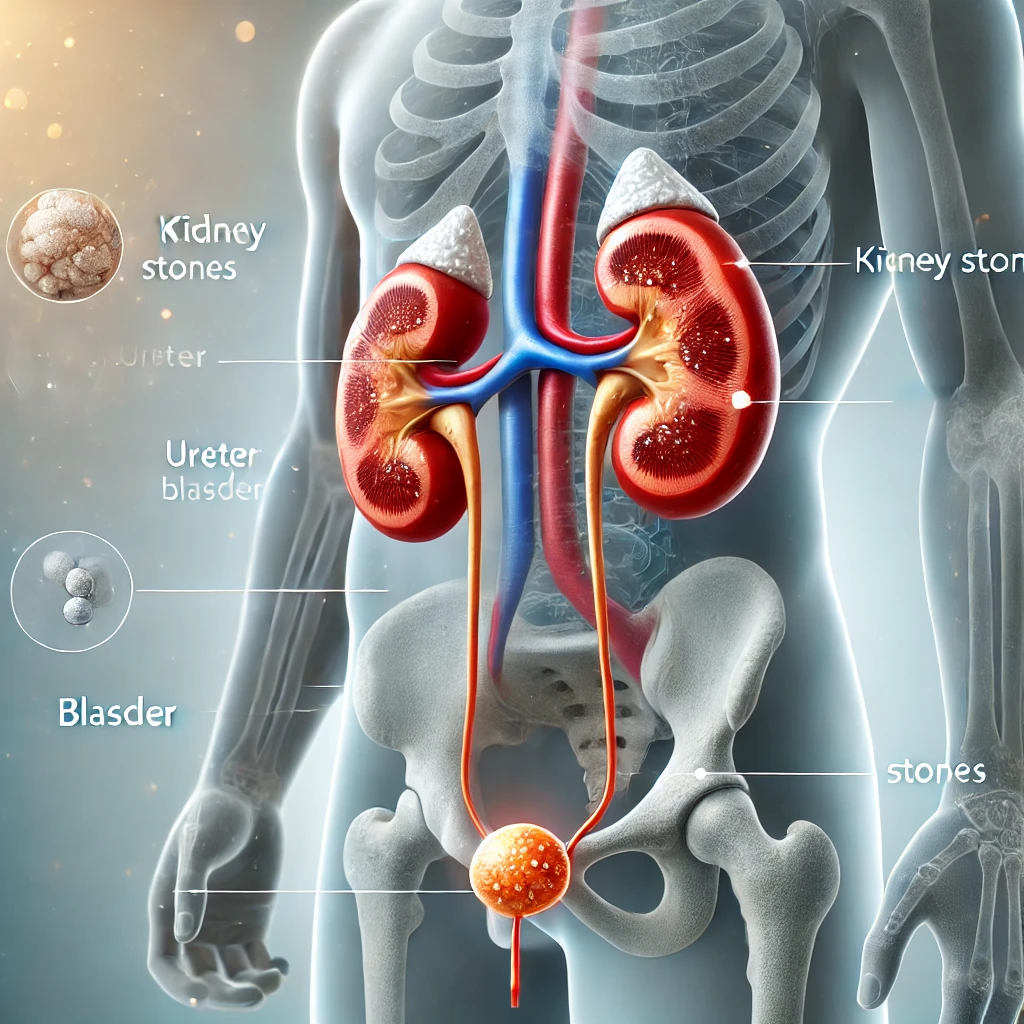
Kidney stones are a common health issue in Nepal, affecting people of all ages. These hard deposits of minerals and salts form in the kidneys and can cause severe pain and complications if not treated properly. With changing lifestyles, dietary habits, and climate conditions, the incidence of kidney stones in Nepal is rising. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help in preventing and managing this condition effectively.
Causes of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones form when certain substances in urine, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, become concentrated and crystallize. Some common causes include:
- Dehydration – Insufficient water intake leads to concentrated urine, increasing the risk of stone formation.
- Diet – A high intake of oxalate-rich foods (such as spinach, nuts, and chocolates) and excess salt can contribute to kidney stones.
- Genetic Factors – A family history of kidney stones increases the likelihood of developing them.
- Medical Conditions – Conditions such as hyperparathyroidism, urinary tract infections, and metabolic disorders can lead to kidney stone formation.
- Climate – Nepal’s hot and dry regions, particularly in the Terai, contribute to higher dehydration rates, increasing kidney stone cases.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
The symptoms vary depending on the size and location of the stone. Common symptoms include:
- Severe pain in the lower back or side (renal colic)
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Painful urination
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills (if infection is present)
Diagnosis
Doctors diagnose kidney stones using a combination of:
- Medical History & Physical Examination
- Urine Tests – To check for infection and stone-forming substances
- Blood Tests – To measure levels of calcium, uric acid, and kidney function
- Imaging Tests – Ultrasound, X-ray, or CT scan to locate and measure the stones
Treatment Options
The treatment of kidney stones depends on their size, type, and severity of symptoms. Common treatment methods include:
- Increased Fluid Intake – Drinking plenty of water can help flush out small stones naturally.
- Pain Management – Medications such as NSAIDs (Flexon 3 times a day for 5 days) help relieve pain.
- Medications – Certain drugs may help dissolve stones or prevent their formation.
- Medical Procedures:
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) – Uses shock waves to break large stones into smaller pieces.
- Ureteroscopy – A thin tube is inserted through the urethra to remove or break the stone.
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy – A minimally invasive surgery for larger stones.
Prevention of Kidney Stones
Preventing kidney stones involves lifestyle and dietary modifications:
- Drink at least 2-3 liters of water daily.
- Reduce salt and oxalate-rich foods in your diet.
- Maintain a balanced diet with adequate calcium.
- Avoid excessive consumption of red meat and processed foods.
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight.
Kidney Stone Treatment in Nepal
Nepal has several hospitals and clinics specializing in kidney stone treatment. Advanced diagnostic and treatment facilities, including ESWL and minimally invasive surgeries, are available in major cities such as Kathmandu, Pokhara, and Chitwan. However, rural areas still face challenges in accessing specialized care.
Conclusion
Kidney stones are a growing health concern in Nepal, but they can be prevented and effectively managed with early diagnosis and proper treatment. Raising awareness about hydration, diet, and medical care can help reduce the burden of kidney stone-related complications in the country.
If you experience symptoms of kidney stones, seek medical advice promptly to prevent severe complications. For consultations and expert care, visit our clinic or book an appointment today.
📞 01-4531078 or 01-4543386
Book USG