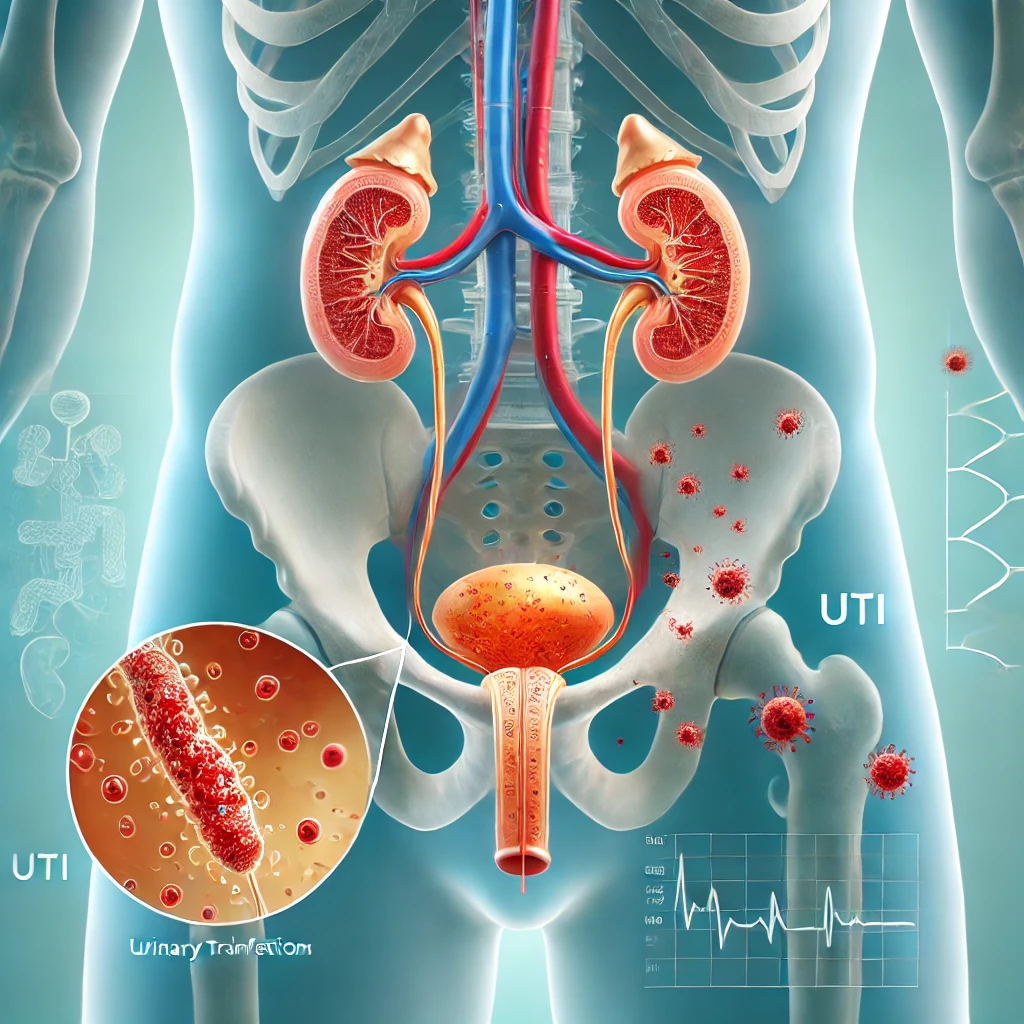
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is a common bacterial infection that affects the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. It can occur in both men and women, but women are more susceptible due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to enter the urinary tract more easily.
Causes of UTI
UTIs are primarily caused by bacteria, with Escherichia coli (E. coli) being the most common culprit. Other contributing factors include:
- Poor personal hygiene
- Holding urine for long periods
- Dehydration and inadequate fluid intake
- Sexual activity
- Use of catheters or urinary tract obstructions (such as kidney stones)
- Weak immune system or underlying health conditions like diabetes
Symptoms of UTI
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain or lower abdominal discomfort
- Fever and chills (if the infection reaches the kidneys)
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
Diagnosis & Treatment
To diagnose a UTI, a doctor may recommend a urine test to check for bacteria, white blood cells, or other indicators of infection. In recurrent or complicated cases, urine culture or imaging tests may be required.
Treatment:
- Antibiotics: Prescribed based on the severity and type of bacteria causing the infection.
- Increased Fluid Intake: Helps flush out bacteria from the urinary system.
- Pain Relievers: May be used to reduce discomfort during urination.
Preventing UTI
- Stay well-hydrated and urinate frequently.
- Maintain proper hygiene, especially after using the toilet.
- Empty the bladder completely after intercourse.
- Avoid excessive use of irritants like harsh soaps and feminine hygiene sprays.
- Wear breathable cotton underwear to reduce moisture buildup.
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Recurrent UTIs are defined as having two or more infections within six months or three or more within a year. They are more common in women due to anatomical factors but can also affect men. Causes include incomplete bladder emptying, hormonal changes, a weakened immune system, kidney stones, or improper hygiene practices. Symptoms often mirror those of a regular UTI—burning urination, frequent urges to urinate, and pelvic discomfort. Preventive measures include staying well-hydrated, urinating after intercourse, maintaining good hygiene, and, in some cases, taking prescribed low-dose antibiotics. If you experience recurrent UTIs, consult a doctor to determine the underlying cause and receive proper treatment
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience UTI symptoms that persist or worsen despite home remedies, seek medical attention. Early treatment can prevent complications such as kidney infections.
Expert Care at Advanced Poly Clinic
At Advanced Poly Clinic, our experienced doctors provide accurate diagnosis and effective treatment for UTIs. If you suspect a urinary tract infection, consult our specialists for prompt care and advice.
Stay informed, stay healthy!
📞 01-4531078 or 01-4543386