Hepatitis
Introduction
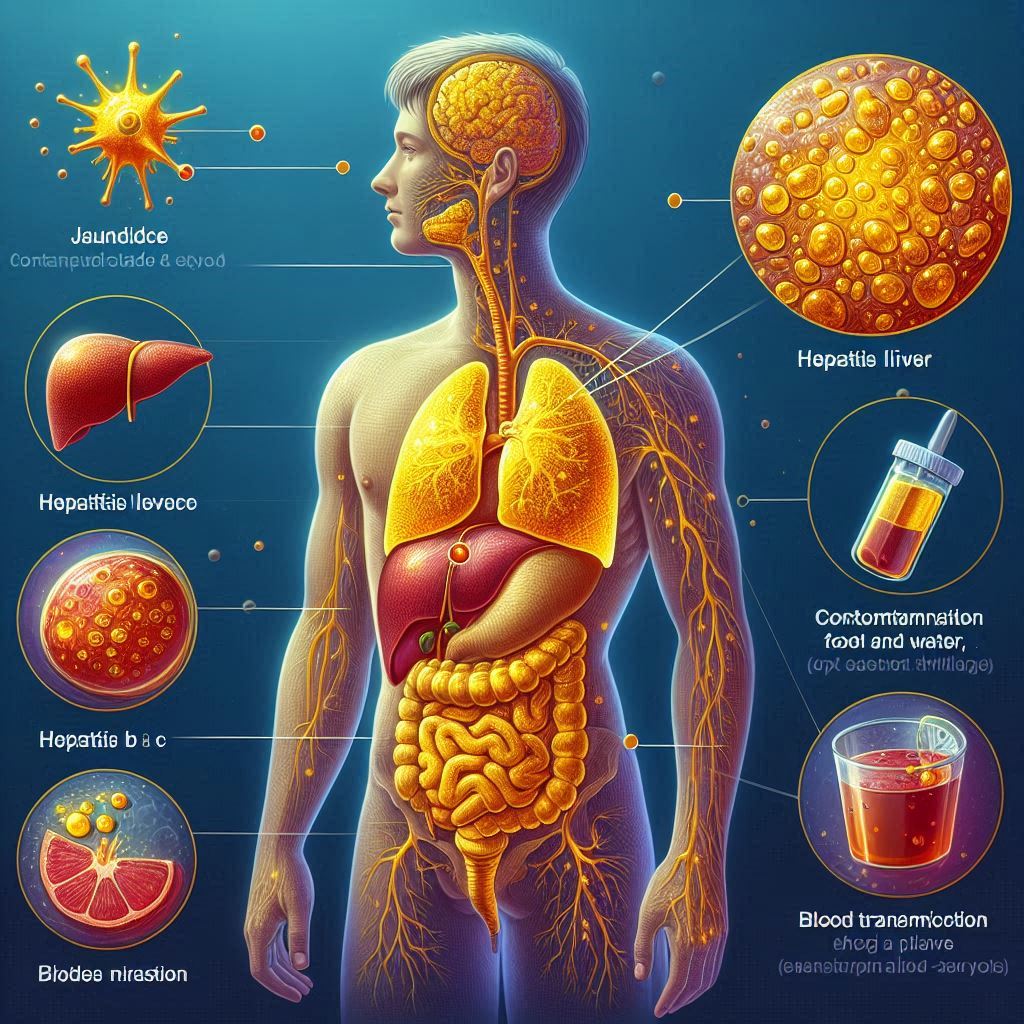
Jaundice is a common medical condition in Nepal, often linked to liver diseases such as Hepatitis A, B, C, and E. It causes yellowing of the skin and eyes due to increased bilirubin levels in the blood. While some forms of hepatitis are self-limiting, others can lead to chronic liver disease and severe complications.
Causes and Transmission
Jaundice itself is a symptom rather than a disease. The major causes include:
- Hepatitis A and E – Spread through contaminated food and water (fecal-oral route).
- Hepatitis B and C – Transmitted through blood, unprotected sex, sharing needles, and from mother to child during childbirth.
Symptoms of Jaundice and Hepatitis
- Yellowing of skin and eyes
- Dark-colored urine and pale stools
- Fatigue and weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain, particularly in the liver region
- Fever (common in Hepatitis A and E)
- Unintentional weight loss
Types of Hepatitis and Their Impact
Hepatitis A
- Acute, short-term infection.
- Common in Nepal due to poor sanitation and contaminated food.
- Preventable with the Hepatitis A vaccine.
Hepatitis B
- Can cause chronic infection leading to liver cirrhosis or liver cancer.
- Preventable with the Hepatitis B vaccine.
- Requires antiviral medications for chronic cases.
Hepatitis C
- Silent infection, often detected at a later stage.
- Major cause of chronic liver disease.
- No vaccine available, but curable with antiviral treatment.
Hepatitis E
- Similar to Hepatitis A but more severe in pregnant women.
- Common in Nepal due to contaminated drinking water.
- Usually self-limiting but can cause complications.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Blood Tests – Check liver enzymes and specific viral markers.
- Ultrasound or Imaging Tests – Assess liver health and detect complications.
- Supportive Care – Hydration, rest, and symptom management for Hepatitis A and E.
- Antiviral Therapy – Used for Hepatitis B and C to prevent liver damage.
Prevention Strategies
- Vaccination – Hepatitis A and B vaccines are highly effective.
- Safe Drinking Water and Hygiene – Reduces the risk of Hepatitis A and E.
- Safe Blood Transfusion and Sterile Needles – Prevents Hepatitis B and C transmission.
- Protected Sexual Practices – Reduces the risk of Hepatitis B and C.
Challenges in Nepal
- Limited Access to Vaccination in Remote Areas
- Poor Sanitation and Unsafe Drinking Water
- Lack of Awareness About Hepatitis B and C
- Costly Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis Cases
Conclusion
Jaundice due to viral hepatitis is a significant health issue in Nepal. While Hepatitis A and E are largely preventable through better sanitation, Hepatitis B and C require early detection and lifelong management. Public awareness, vaccination, and hygiene practices are key to reducing the burden of hepatitis-related jaundice in Nepal. If you experience symptoms of jaundice, seek medical attention promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.
📞 01-4531078 or 01-4543386