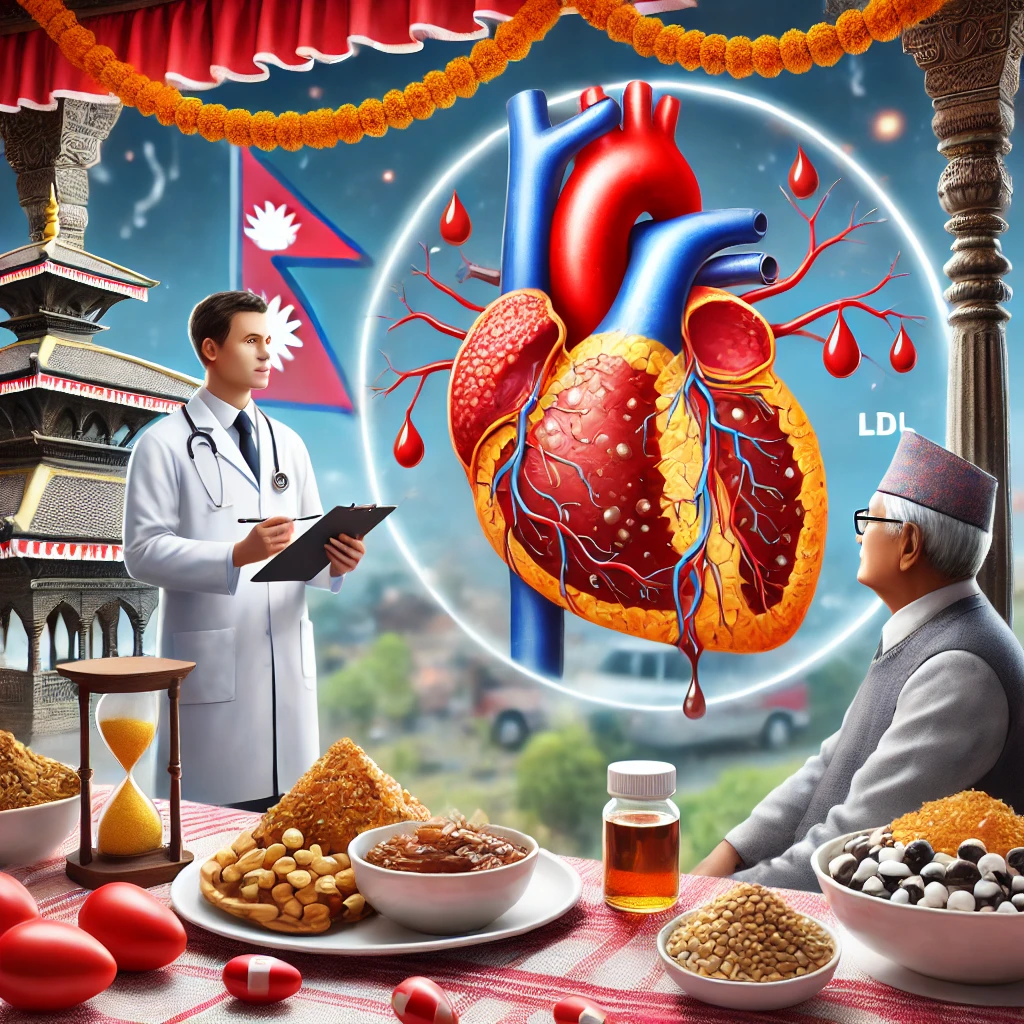
What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in your blood. Your body needs it to build healthy cells, but too much cholesterol can increase your risk of heart disease. Cholesterol is carried in the blood by lipoproteins:
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL): Often called “bad” cholesterol, high levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Known as “good” cholesterol, it helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream.
- Triglycerides: Another type of fat in the blood that can contribute to heart disease if levels are too high.
What is Dyslipidemia?
Dyslipidemia refers to abnormal levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. This includes:
- High LDL (bad cholesterol)
- Low HDL (good cholesterol)
- High triglycerides
- A combination of these conditions
Why is Cholesterol Important?
In Nepal, cardiovascular diseases are a leading cause of death. Unhealthy diets, sedentary lifestyles, and genetic predisposition contribute to high cholesterol levels. Factors such as high consumption of saturated fats, smoking, and lack of physical activity increase the risk of dyslipidemia.
Risk Factors for High Cholesterol in Nepal
- Diet: High intake of fried foods, saturated fats, and processed foods
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of regular exercise and physical activity
- Obesity: Excess body weight can lead to high LDL and triglycerides
- Smoking & Alcohol: Smoking lowers good cholesterol, and excessive alcohol consumption raises triglycerides
- Genetics: Family history of high cholesterol increases the risk
- Underlying Conditions: Diabetes, hypothyroidism, and kidney disease can contribute to dyslipidemia
Symptoms of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol itself does not cause symptoms. It is often diagnosed through a blood test. However, prolonged high cholesterol can lead to serious complications like:
- Heart attacks
- Strokes
- Peripheral artery disease
- Fatty deposits in the liver
Diagnosis & Recommended Cholesterol Levels
A lipid profile test measures different types of cholesterol in your blood. Recommended levels:
- LDL Cholesterol: Below 100 mg/dL (optimal)
- HDL Cholesterol: Above 40 mg/dL for men and 50 mg/dL for women
- Triglycerides: Below 150 mg/dL
- Total Cholesterol: Below 200 mg/dL
Preventing & Managing Dyslipidemia
- Healthy Diet: Reduce saturated fats, increase fiber, and eat heart-friendly foods like vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- Exercise Regularly: At least 30 minutes of physical activity most days of the week.
- Quit Smoking: Improves HDL cholesterol and overall heart health.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol raises triglyceride levels.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Helps balance cholesterol levels.
- Regular Checkups: Get a lipid profile test at least once a year, especially if at high risk.
Treatment Options
For people with very high cholesterol or those at risk of heart disease, doctors may prescribe:
- Statins: To lower LDL cholesterol (Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin are most commonly prescribed in Nepal)
- Fibrates: To lower triglycerides (Fenofibrates – TGR 160mg is most commonly prescribed in Nepal)
- Niacin & Omega-3 Supplements: To help manage cholesterol levels
Conclusion
Dyslipidemia is a growing concern in Nepal, with increasing cases linked to lifestyle choices and dietary habits. Regular checkups, a healthy diet, and lifestyle changes can help manage cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease. Moreover, high cholesterol does not cause any symptoms, and they are known as silent killers. The only way to know if you have dyslipidemia (high cholesterol) is by doing your blood test.
Call us to find out about Lipid Profile blood test.
📞 01-4531078 or 01-4543386